랜섬웨어 문제이다.
- 헤더
- 구성: sha256(basename) 32B|| local nonce 12B || sha256(DATA) 32B을 CHACHA20으로 암호화
- 바디
- 메인데이터 CHACHA20으로 암호화
- 푸터
- RSA 평문: sha256(basename) 32B||sha256(local nonce) || global nonce 12B || key 32B = 총 108B
- RSA 암호문: e=65537, 하드코딩된 N(1024-bit) 사용으로 정리할수있다.
여기서 가장먼저 해야될것은 헤더에서 chacha20 스트림암호화를 이용해 local nonce를 뽑아내는거였다.
식으로 나타내면
KS XOR M1 =C1
KS XOR M2 =C2 형태로 나타낼수있다.(여기서 KS는 key와 global nonce, M은 filename+local_nonce+sha256(file data)이다.)
이 암호의 경우 XOR로 이루어져있는데 만약 두다항식을 XOR을한다면 KS는 같은값이라 지워지게 된다.
결국 M1 XOR M2= C1 XOR C2형태로 되는것
근데 여기서 중요한점이 filename의 길이가 다르다는것이다.
즉 filename+nonce값인데
1의경우 defence.png
2의경우 flag.png
defence.png
flag.png
를 해보면 M1은 png글자만큼 차이가 나는데 즉 C1 XOR M1(PNG 글자중하나를 하면) = M2의 글자를 알수있게 된다. 여기서 nonce값의 코드를 보면

다음처럼 시간에 관한 랜덤값을 12번 넣게되는데 어셈을볼때 랜덤값에서 1바이트만 값을넣게된다 즉 0xff이하의 값이 12번 동일하게 들어가는것이다.
그렇다면 nonce값이 만약 0xa0으로 채워졌다면 0xa0a0a0a0a0a0a0a0a0a0처럼 반복될것이고 하나를 알게되면 전체를 알수있게된다.
그렇게해서 m2의 nonce값을 구하면 이번엔 반대로 구해진 m2의 nonce값을 가지고 xor을 하면 m1을 구할수있게된다.
두개모두의 nonce값을 획득가능해진다.
import os
MARKER = b'CCE2025'
def basename_from_encrypted_path(p):
n = os.path.basename(p)
return n[:-8] if n.endswith('.CCE2025') else n
def read_header_ct(p):
d = open(p, 'rb').read()
i = d.find(MARKER)
if i <= 0:
raise ValueError('marker not found')
return d[:i]
def xor(a,b):
m = min(len(a),len(b)); return bytes([a[i]^b[i] for i in range(m)])
f1 = 'defence.png.CCE2025'
f2 = 'flag.png.CCE2025'
h1 = read_header_ct(f1)
h2 = read_header_ct(f2)
b1s = basename_from_encrypted_path(f1).encode()
b2s = basename_from_encrypted_path(f2).encode()
L1, L2 = len(b1s), len(b2s)
# 1) 파일명 구간에서 키스트림 KS 일부
KS1 = bytes([h1[i]^b1s[i] for i in range(min(L1, len(h1)))]) # KS[0:L1]
# 2) 파일2 논스 앞 3바이트 복구 (pos2 = L2 .. L2+2 < L1)
n2_0 = h2[L2+0] ^ KS1[L2+0]
n2_1 = h2[L2+1] ^ KS1[L2+1]
n2_2 = h2[L2+2] ^ KS1[L2+2]
if not (n2_0 == n2_1 == n2_2):
raise ValueError("반복 바이트 가정 불일치: 파일2 논스 앞 3바이트가 서로 다릅니다.")
b2 = n2_0
# 3) 겹침 구간 XOR로 n1⊕n2의 바이트값 v 확인 (여기서는 a4)
overlap = xor(h1, h2)[max(L1, L2):min(L1+12, L2+12)]
if not overlap:
raise ValueError("논스 겹침 없음")
v = overlap[0]
if not all(x == v for x in overlap):
raise ValueError("겹침 XOR가 상수가 아님 → 반복 바이트 가정 불가")
# 4) b1 = b2 ⊕ v
b1 = b2 ^ v
nonce1 = bytes([b1]*12)
nonce2 = bytes([b2]*12)
print("local_nonce(file1) =", nonce1.hex())
print("local_nonce(file2) =", nonce2.hex())
print(f"check v=0x{v:02x}, b1=0x{b1:02x}, b2=0x{b2:02x}")

나온결과
자여기서 local nonce를 구했으니 이제 RSA로 넘어간다.
RSA에 암호화되는 구조는
M1=sha256(filename1)+sha256(local nonce)+global nonce+ key
M2=sha256(filename2)+sha256(local nonce)+global nonce+ key
이제 여기선 공통값이 존재하는데 global nonce+key이다. 이걸 x로두고 filename과 localnonce는 값을 아니 이 공통된 x를 구하면된다.
(x+m1)^e-c1 mod n =0
(x+m2)^e-c2 mod n =0으로 다항식을 세워서 전개를하면
(x-a)p`(x) mod n
(x-a)q`(x) mod n 이런식으로 되어 공통된 (x-a)를 통해 x값을 구할수잇게된다.
https://github.com/jvdsn/crypto-attacks/blob/master/shared/polynomial.py
crypto-attacks/shared/polynomial.py at master · jvdsn/crypto-attacks
Python implementations of cryptographic attacks and utilities. - jvdsn/crypto-attacks
github.com
을 활용하여 half gcd를 통해 값을구했다. 값을 구한뒤 LLM을 통해 그값이 맞는지 확인하는 코드가 포함되어있다.
import hashlib
from sage.all import *
from math import lcm
import logging
# fast_crt 함수
def fast_crt(X, M, segment_size=8):
"""
Uses a divide-and-conquer algorithm to compute the CRT remainder and least common multiple.
:param X: the remainders
:param M: the moduli (not necessarily coprime)
:param segment_size: the minimum size of the segments (default: 8)
:return: a tuple containing the remainder and the least common multiple
"""
assert len(X) == len(M)
assert len(X) > 0
while len(X) > 1:
X_ = []
M_ = []
for i in range(0, len(X), segment_size):
if i == len(X) - 1:
X_.append(X[i])
M_.append(M[i])
else:
X_.append(crt(X[i:i + segment_size], M[i:i + segment_size]))
M_.append(lcm(*M[i:i + segment_size]))
X = X_
M = M_
return X[0], M[0]
def _polynomial_hgcd(ring, a0, a1):
assert a1.degree() < a0.degree()
if a1.degree() <= a0.degree() / 2:
return 1, 0, 0, 1
m = a0.degree() // 2
b0 = ring(a0.list()[m:])
b1 = ring(a1.list()[m:])
R00, R01, R10, R11 = _polynomial_hgcd(ring, b0, b1)
d = R00 * a0 + R01 * a1
e = R10 * a0 + R11 * a1
if e.degree() < m:
return R00, R01, R10, R11
q, f = d.quo_rem(e)
g0 = ring(e.list()[m // 2:])
g1 = ring(f.list()[m // 2:])
S00, S01, S10, S11 = _polynomial_hgcd(ring, g0, g1)
return S01 * R00 + (S00 - q * S01) * R10, S01 * R01 + (S00 - q * S01) * R11, S11 * R00 + (S10 - q * S11) * R10, S11 * R01 + (S10 - q * S11) * R11
def fast_polynomial_gcd(a0, a1):
"""
Uses a divide-and-conquer algorithm (HGCD) to compute the polynomial gcd.
More information: Aho A. et al., "The Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms" (Section 8.9)
:param a0: the first polynomial
:param a1: the second polynomial
:return: the polynomial gcd
"""
# TODO: implement extended variant of half GCD?
assert a0.parent() == a1.parent()
if a0.degree() == a1.degree():
if a1 == 0:
return a0
a0, a1 = a1, a0 % a1
elif a0.degree() < a1.degree():
a0, a1 = a1, a0
assert a0.degree() > a1.degree()
ring = a0.parent()
# Optimize recursive tail call.
while True:
logging.debug(f"deg(a0) = {a0.degree()}, deg(a1) = {a1.degree()}")
_, r = a0.quo_rem(a1)
if r == 0:
return a1.monic()
R00, R01, R10, R11 = _polynomial_hgcd(ring, a0, a1)
b0 = R00 * a0 + R01 * a1
b1 = R10 * a0 + R11 * a1
if b1 == 0:
return b0.monic()
_, r = b0.quo_rem(b1)
if r == 0:
return b1.monic()
a0 = b1
a1 = r
def polynomial_gcd_crt(a, b, factors):
"""
Uses the Chinese Remainder Theorem to compute the polynomial gcd modulo a composite number.
:param a: the first polynomial
:param b: the second polynomial
:param factors: the factors of m (tuples of primes and exponents)
:return: the polynomial gcd modulo m
"""
assert a.base_ring() == b.base_ring() == ZZ
gs = []
ps = []
for p, _ in factors:
zmodp = Zmod(p)
gs.append(fast_polynomial_gcd(a.change_ring(zmodp), b.change_ring(zmodp)).change_ring(ZZ))
ps.append(p)
g, _ = fast_crt(gs, ps)
return g
def polynomial_xgcd(a, b):
"""
Computes the extended GCD of two polynomials using Euclid's algorithm.
:param a: the first polynomial
:param b: the second polynomial
:return: a tuple containing r, s, and t
"""
assert a.base_ring() == b.base_ring()
r_prev, r = a, b
s_prev, s = 1, 0
t_prev, t = 0, 1
while r:
try:
q = r_prev // r
r_prev, r = r, r_prev - q * r
s_prev, s = s, s_prev - q * s
t_prev, t = t, t_prev - q * t
except RuntimeError:
raise ArithmeticError("r is not invertible", r)
return r_prev, s_prev, t_prev
def polynomial_inverse(p, m):
"""
Computes the inverse of a polynomial modulo a polynomial using the extended GCD.
:param p: the polynomial
:param m: the polynomial modulus
:return: the inverse of p modulo m
"""
g, s, t = polynomial_xgcd(p, m)
return s * g.lc() ** -1
def max_norm(p):
"""
Computes the max norm (infinity norm) of a polynomial.
:param p: the polynomial
:return: a tuple containing the monomial degrees of the largest coefficient and the coefficient
"""
max_degs = None
max_coeff = 0
for degs, coeff in p.dict().items():
if abs(coeff) > max_coeff:
max_degs = degs
max_coeff = abs(coeff)
return max_degs, max_coeff
# 제공된 데이터
N = Integer(0xd7dd82fdc6921c455c92033bb6f51045afe2ba908c3c13c643b7bc87f96135dbe9a97c364ad5a82e47a1556860f170147a6f9f9fdaf4f308fc6bccf57a7d86582b2794c19c90839c3cfcbe75edbc57e7125e378ccce1d6c320e6983361fd6cb1e5ae78520384979dca7461c7b2574153d9ff4bdb47e60bbe9728b9d51c491a69)
e = 65537
C1 = Integer(0x1a28767b84da630beeac79161f6f79c6f08e6625f638b2ffcdb7816706bab9448c6abbcff73ac35992dcbbdc88d38aebb8f869ebeaa71e4e98b58994060842bc89cb4f37faf7a6716411e25b5044368eb4ce55d852261a49c792350d54dafddce6cb47f7dec9c1ebb2f8c3ad6578754e94c62f26c0a96bd82d698286f75a2b2e)
C2 = Integer(0xc07b6461945c100fa10581dbaffd62177892f459296504e7316523cd9b593b164ebe413b1dbb7dc99244ea7f7c8d49b437be9a45948d9f4a71b91284dfb766a02468fccdf1e18cc3e8f5e7db8fe7693dd8c57d1097064d701a1813f5c87b405654566e47eda65f9410e30c0a36a2e2bcd39dd27074fceb45d08b109f532a4156)
hash_file1 = Integer(0x6b434d33ee0d3840c2ff29a8b161ac7af7a0f2dc4476b0c49f36cf2f6483c22b)
hash_file2 = Integer(0x8fce54c8306d297af0088b0531a21aa395e85d3fa1bc620e188265ca91c6e001)
nonce1 = bytes.fromhex("f8f8f8f8f8f8f8f8f8f8f8f8")
nonce2 = bytes.fromhex("5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c")
hash_nonce1 = Integer(int(hashlib.sha256(nonce1).hexdigest(), 16))
hash_nonce2 = Integer(int(hashlib.sha256(nonce2).hexdigest(), 16))
shift_Hf = 8*76
shift_Hl = 8*44
# x := Gn<<256 + Key (미지수), K_i := Hf_i<<shift_Hf + Hl_i<<shift_Hl (상수)
K1 = (hash_file1 << shift_Hf) + (hash_nonce1 << shift_Hl)
K2 = (hash_file2 << shift_Hf) + (hash_nonce2 << shift_Hl)
P.<X> = PolynomialRing(Zmod(N))
F1 = (X + K1)^e - C1
F2 = (X + K2)^e - C2
G = fast_polynomial_gcd(F1, F2)
print(G)
# 근 A 계산 (가능하면 모닉을 가정하되, 일반 계수도 처리)
try:
a0 = Integer(G[0])
a1 = Integer(G[1])
except Exception:
raise RuntimeError("선형 다항식이 아닙니다. GF(p)에서 근을 구해 CRT로 합치세요.")
if gcd(a1, N) != 1:
raise RuntimeError("X의 계수가 비가역입니다. GF(p) 방식(소수체에서 근 구해 CRT)으로 진행하세요.")
A = (-a0 * inverse_mod(a1, N)) % N # A = (global_nonce << 256) + key
# 분리: global_nonce(12B=96bit), key(32B=256bit)
global_nonce = (A >> (8*32)) & ((1 << (8*12)) - 1)
key = A & ((1 << (8*32)) - 1)
print(f"global_nonce = 0x{int(global_nonce):x}")
print(f"key = 0x{int(key):x}")
# 검증: (A + K1)^e ≟ C1 (mod N), (A + K2)^e ≟ C2 (mod N)
ok1 = pow(int(A + K1), int(e), int(N)) == int(C1)
ok2 = pow(int(A + K2), int(e), int(N)) == int(C2)
print(f"verify C1: {ok1}, verify C2: {ok2}")
if not (ok1 and ok2):
raise RuntimeError("검증 실패: 링 Zmod(N)에서 얻은 근이 올바르지 않습니다. GF(p)→CRT 절차를 사용하세요.")
구한 값들
구한 값을 이용해 gpt 복호화 코드짜줘
# pip install cryptography
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.ciphers import Cipher, algorithms
from pathlib import Path
import hashlib
# 복구된 값들
KEY_HEX = "fe3201004fa05a3ac464174cf9e321af8e04fd4e4e3f3c5c2723b7be644a6f04"
GLOBAL_NONCE_HEX = "606060606060606060606060"
LOCAL_NONCE_HEX = "5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c5c" # 사용자 제공
IN_FILE = Path("flag.png.CCE2025")
OUT_FILE = Path("flag.png.recovered")
def chacha20_ietf(key: bytes, nonce12: bytes, data: bytes) -> bytes:
nonce16 = (0).to_bytes(4, "little") + nonce12 # counter=0, 12B nonce
algo = algorithms.ChaCha20(key, nonce16)
cipher = Cipher(algo, mode=None)
return cipher.decryptor().update(data)
def main():
data = IN_FILE.read_bytes()
magic = b"CCE2025"
m1 = data.find(magic)
if m1 < 0: raise RuntimeError("첫 번째 마커 없음")
m2 = data.find(magic, m1 + len(magic))
if m2 < 0: raise RuntimeError("두 번째 마커 없음")
header_ct = data[:m1]
body_ct = data[m1 + len(magic):m2]
# tail = data[m2 + len(magic):] # RSA 암호문(불필요)
key = bytes.fromhex(KEY_HEX)
gnonce = bytes.fromhex(GLOBAL_NONCE_HEX)
lnonce = bytes.fromhex(LOCAL_NONCE_HEX)
# 본문 복호화 (key + local_nonce)
body_pt = chacha20_ietf(key, lnonce, body_ct)
# 헤더 복호화 (key + global_nonce) → basename | local_nonce(12B) | sha256(body)(32B)
header_pt = chacha20_ietf(key, gnonce, header_ct)
if len(header_pt) < 44: raise RuntimeError("헤더 길이 비정상")
header_hash = header_pt[-32:]
header_lnonce = header_pt[-44:-32]
basename = header_pt[:-44]
# 무결성 및 nonce 검증
calc_hash = hashlib.sha256(body_pt).digest()
if calc_hash != header_hash:
raise RuntimeError("sha256(body) 불일치")
if header_lnonce != lnonce:
raise RuntimeError("local_nonce 불일치")
# 원래 파일명으로 저장(실패 시 기본 이름)
try:
name = basename.decode("utf-8")
out = IN_FILE.with_name(name) if name else OUT_FILE
except UnicodeDecodeError:
out = OUT_FILE
out.write_bytes(body_pt)
print(f"복호화 성공: {out}")
print(f"local_nonce = 0x{lnonce.hex()}")
print(f"sha256(body)= 0x{calc_hash.hex()} (헤더와 일치)")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()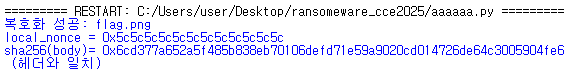

이것은 암호학문제인가 리버싱문제인가.. 많은 배움이 있었습니다.
'리버싱!' 카테고리의 다른 글
| privacy-i 삭제 일대기 (1) | 2025.11.21 |
|---|---|
| cce2025 (4) | 2025.08.19 |
| CCE 준비 (2) | 2025.08.08 |
| justCTF2025 (0) | 2025.08.03 |
| UIUCTF 2025-풀이 (3) | 2025.07.26 |

